What is SaaS? Essentially, “Software as a Service” or SaaS is a software distribution model. It is one of the ways a cloud provider hosts applications and lets people use them over the internet. SaaS, a market currently worth in excess of $100 billion annually, and predicted by some to grow by as much as $200 billion by 2024.
SaaS applications are being widely adopted both by B2B and B2C users wordwide, and for good reason. That’s why we’ve put together this simple guide, so you can get up to speed with everything you need to learn about this crucial software distribution model. Let’s not waste time and dive straight into the content!
Table of contents
What is SaaS in simple terms?

In its most simple terms, SaaS is simply software that lives in the cloud. That’s it!
However, to understand more about what SaaS is, we first need to know what life was like before SaaS products existed. In the past, if you wanted software, you downloaded it to your computer and installed it. Anything related to that software was stored on your machine.
So what happens if you need access to that software from somewhere else? This is where SaaS comes in. SaaS is essentially software that lives in the cloud and not on a specific machine.
This means you can access it from anywhere, anytime. However, unlike traditional software, which you pay for once, SaaS products are typically priced on a monthly basis as the SaaS owner takes care of everything from hosting and maintaining all the hardware related to the product.
As the world moves, embracing cloud software more and more, expect to see the term “SaaS” being more widely used. Over the past few years, SaaS products have grown massively due to their convenience, ease of access, and affordable pricing.
When building a SaaS, focus on solving a problem!
How does SaaS work?
SaaS applications work with the help of a cloud delivery model that involves a software provider running the applications with the support of servers, databases, and networking resources. Other cloud computing-based software distribution models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
The SaaS application is hosted in the provider’s data center and is made accessible to devices via a network connection. Most SaaS applications run perfectly on web browsers. This way, companies that use SaaS applications don’t have to spend time or money building a setup and investing in regular maintenance.
All they have to do is pay for the subscription to gain access to a ready-made software solution. One can also relate SaaS to Application Service Provider or ASP. It’s because the provider delivers the software to approved end-users over a network.
Another SaaS model worth mentioning here is software-on-demand. In this, the provider gives a single copy of the software created for the SaaS distribution. The source code on the software is the same across the user base, and the new updates are rolled out at the same time and to all customers.
Most SaaS applications you will come across use a multi-tenant approach. In other words, the host servers will run a single instance of the SaaS application, and the customers or subscribers will be served through it.
The idea is to run the same application (with the same version and configuration) across all the subscribers, customers, or tenants. However, the data generated by different tenants will vary depending on their usage.
The multi-tenant approach is by far the most efficient SaaS application architecture as it involves easy application maintenance. You can find and fix the bugs faster and implement updates more efficiently.
Not just that, it also keeps the application and customers from security, speed, and privacy issues. But why should businesses invest in creating a SaaS for their organizations? Let’s find out!
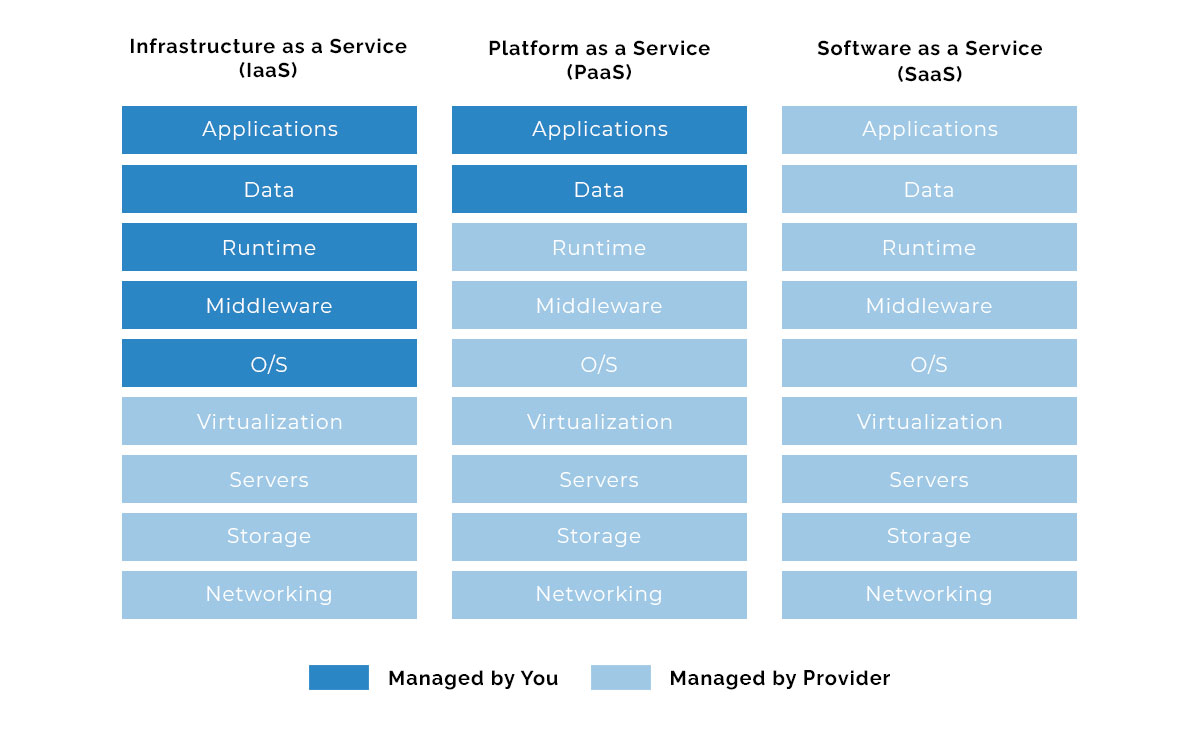
Difference between SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS
Major advantages of using SaaS
There are several advantages of using SaaS in an organization. Some of the essential benefits of SaaS applications are as follows:
1. Real money saver
SaaS helps organizations save money on infrastructure. There is no need to host the application on their data centers. Businesses can successfully eliminate all expenses on hardware acquisition and maintenance. They don’t have to worry about application licensing or support.
2. Offers vertical scalability
SaaS is essentially a cloud-based service. Therefore, the opportunities to scale are enormous. You can create a SaaS application, get it to your user base, and keep on adding more useful features to it. Customers that need the features will pay to gain access. They can add features on-demand making SaaS open for vertical scalability.
3. Accessibility
The incessant development in internet and mobile technologies has helped establish a solid foundation for SaaS market growth. The internet has made it easier for SaaS vendors to deliver applications and allow users to access them whenever they want, from any location on the planet.
4. Personalization
SaaS applications are known for providing businesses with customizations that suit their requirements. The applications can be customized to make them work seamlessly with other business applications. This is extremely useful when one has a business that needs several applications to work together.
5. Flexible payments
SaaS eliminates the need to install additional resources to support an application. The SaaS offering is capable enough to lower the recurring operating expenses and help businesses run efficiently. As a business owner, you can subscribe or unsubscribe to a SaaS offering whenever you want. Stay with us as we discuss the various SaaS pricing models in a moment.
Challenges of using SaaS

Since SaaS is run and managed by a third-party vendor, there arise several risks and challenges worth mentioning in this post. Let’s discuss them, in brief, to get acquainted with the potential difficulties SaaS could develop in your business.
1. Migration
Switching vendors can be a massive problem with SaaS. When you change vendors, you will have to move a large amount of data. This can be challenging, especially if the data transfer process between the cloud providers is complicated. Make sure you choose SaaS applications that have robust technologies in place to help customers migrate their data.
2. Compliance
SaaS solutions need to meet special regulatory compliance requirements. Regulations like HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, FISMA, and others help SaaS providers function within the industry standards. A cloud-based service that doesn’t meet the industry-required regulatory standards can cause significant issues in your company. Your business might get subjected to risks and penalties.
3. Data privacy
We all have read news of data breaches happening every few weeks. Cloud providers might suffer data breaches which generally result in loss of customer information. If you choose a SaaS application hosted on a weak cloud service, the chances of your sensitive data getting leaked increase.
4. Update rollout
Versioning can make customers lose control over the application. Customers have no say when the provider adopts a new version of the application. Customers will have to deal with the update rollout regardless of whether or not they need it. Changes might make your organization invest time and money into training.
5. Lack of control
Several issues that are beyond customer control can make your SaaS experience not so pleasing. Although customers don’t have to manage resources to run the cloud servers, handing off the responsibility also sometimes doesn’t help. You cannot verify the efficacy of the security controls. There’s no way you can analyze the information about their data and services. Most importantly, customers don’t have any control over the responses when an issue occurs.
Important SaaS pricing models

You can choose from several SaaS pricing models that suit your business. Here are some of the most used subscription-based pricing models for SaaS solutions in 2021:
1. Per-user
In this, the price of the subscription is decided based on the number of people that will use the SaaS application. There can be a fixed price for every person that will use it.
2. Storage tiers
The SaaS application might come for free, but the customers will have to pay once they need extra storage or wish to continue using the product.
3. Feature-based tiers
This pricing model depends on the number of features customers demand while using a SaaS application. The application’s pricing might vary with features and functionalities. Customers will have to pay higher prices as they add more features to their application.
4. Freemium
In this, the entry-level tier is free to use, and customers will have to pay once they want to use the restricted functionalities.
5. Flat rate
The SaaS application comes with a full suite of features that can be availed for a fixed monthly or annual subscription fee. This is one of the most used pricing models for SaaS.
6. Free
Lastly, we have free SaaS applications that are free to use. The SaaS providers earn money by putting ads in their applications. Customers that don’t want to see intrusive ads on their application can upgrade to a paid version.
Keep reading!
So, what do you think about using SaaS for your business? Indeed, it’s a great alternative to building your own solution and managing it. But, it also comes with downsides that one should be aware of. We hope we did a good job explaining SaaS from inside and out.
Loved reading this content? Don’t forget to check out other informative posts on the blog!
